What Is an Annular Tear of the Lumbar Disc?
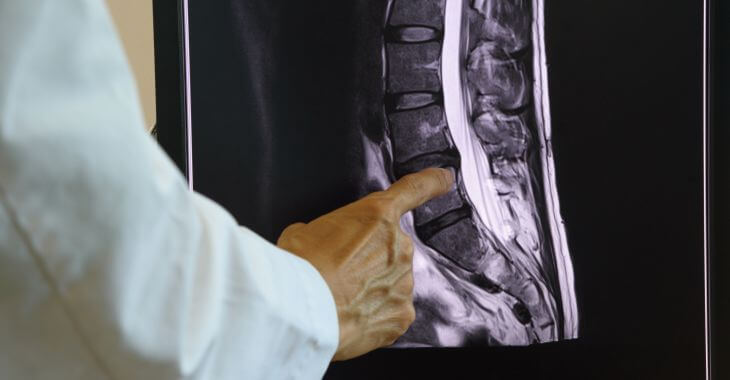
The spinal column is a combination of bone, ligaments, spinal discs, nerves and other components. Injuries, degenerative disease and wear can affect the components of the spinal column, causing pain and dysfunction. An annular tear is one of the conditions that can cause pain, especially in the lower back.
What Is an Annular Tear?
The spinal discs are cushions between the vertebrae, providing shock absorption for the spine. The ligaments that attach the spinal discs to the vertebrae are called the annulus fibrous. This is a circular network of cartilage fibers that cover and hold the softer center of the disc in place.
When the annulus fibrous is damaged from injury or degenerative disease, this is called an annular tear. The annulus fibrous contains many nerve fibers, which can make this condition very painful. The most common discs affected by annular tears are the lumbar discs in the lower spine.
There are different annular tear of lumbar disc types. It depends on what layer of the annulus fibrous ring is damaged. The various types of annular tears include:
- Radial. This is when tears occur from the center of the disc and goes to the outer layer of the disc. Radial annular tears are often caused by degenerative disease and can result in a bulging or herniated disc.
- Concentric. When the outer layers of the disc are torn along the circumference, it is called a concentric annular tear. These are usually caused by injuries or trauma to the disc or spine.
- Peripheral. Tears on the outer layers of the discs from injury or wear from a bone spur are called peripheral tears. These can lead to deterioration of the disc.
An annular tear of a lumbar disc is often painful, regardless of the type. Radial tears may occur slowly with degeneration, while concentric or peripheral tears may cause sudden pain after an injury. All can have similar symptoms, regardless of where and how the tears occur.
Symptoms of Annular Tear of Lumbar Discs
While mild annular tears may not cause immediate pain, most moderate or severe tears will cause pain. For an annular tear of a lumbar disc, the most noticeable symptom will be low back pain. Other symptoms can occur, especially if the disc is bulging or herniated from tears in the ligament, including:
- Sciatica – radiating pain, weakness or tingling down one side of the buttocks and legs
- Radiating burning sensation
- Increased pain when sitting
- Reduced flexibility
Symptoms alone are not enough to diagnose an annular tear of a lumbar disc. Many lumbar spine conditions have similar symptoms – it is necessary to have a doctor perform an exam and tests to determine if you have an annular tear or something else causing your lower back pain.
Causes of Lumbar Disc Annular Tears
Tears to the annulus fibrous ring around the spinal disc can occur due to injury, wear or disease. Small tears can occur over time from general wear, tear and spinal degeneration. Bone spurs can rub against the outer disc, resulting in small peripheral tears. Injuries can also cause annular tears of lumbar discs, including:
- Heavy lifting
- Vehicle accidents
- Constant sitting – working at a desk or driving for a living
- Twisting injuries
- Sports injuries
Whether an annular tear occurs over time or quickly with an accident, it is possible for the tear to heal. However, once an annular tear affects a spinal disc, it is more likely to have subsequent tears or herniation due to a weakened annulus fibrous. For pain relief, many people seek treatment for this condition.
Treatment for Annular Tear of Lumbar Tear
Tears in the outer fibrous shell of lumbar spinal discs can heal on their own, but it can take an extensive recovery period. There is very little blood supply to the annulus fibrous, slowing the repair process. Some types of annular tears may take over a year to heal and activity can reinjure the disc.
Treatments for annular tears in the lumbar discs are usually conservative in the beginning. Your doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory medications to relieve irritation and offer pain relief. Physical therapy, steroid injections, chiropractic treatment and other conservative treatments can offer pain relief.
When conservative treatments are ineffective or if the lumbar disc becomes herniated, more aggressive medical care may be recommended. Surgical repair or replacement of the damaged lumbar disc are options if other less invasive treatments do not allow the disc to repair on its own or relieve the symptoms.
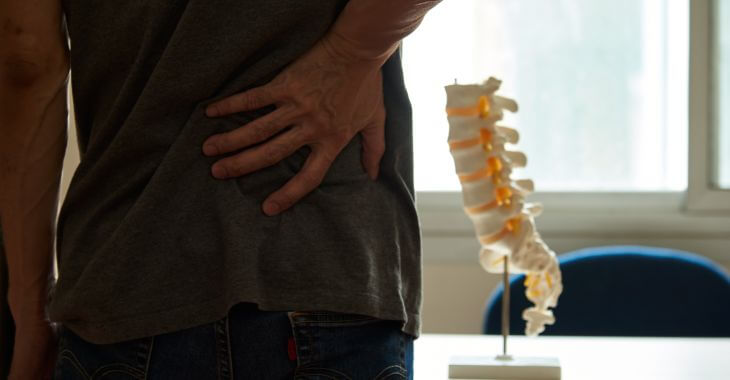
If you have symptoms of an annular tear of lumbar disc, schedule an appointment with your doctor or an orthopedic specialist. A comprehensive exam and possibly x-rays or other imaging may be needed to accurately diagnose an annular tear and begin treatment to offer you relief from your low back pain.
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.



)