Injections for Relief from Sacroiliac Joint Pain

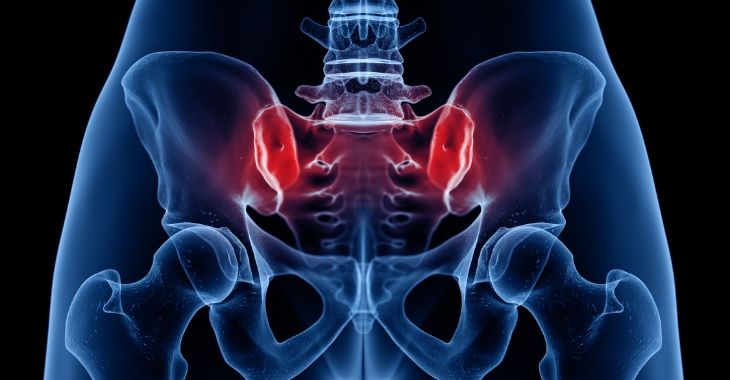
Joint problems are a common cause of pain, but it is not just the joints on your limbs that can have issues. The sacroiliac joints are not visible joints like the wrist, shoulder, elbow or knee, but can have similar issues. These joints are in the lower back, connecting the hip bone and sacrum, the small pieces of bone between the hips and tailbone. When these joints are inflamed or dysfunctional, they can cause pain and weakness through the lower back, hips and legs. One option for treatment is injections in the sacroiliac joint.
Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Pain
The problem with sacroiliac joint pain is that it can mimic other problems in the lumbar region of the back. It can cause sciatica, symptoms that are caused by pressure on the sciatic nerve. This is also a common issue with herniated or injured discs in the lumber region. But when it is a sacroiliac joint issue, some of the symptoms include:
- Lower back pain, from moderate to severe
- Spreading pain through the hips and groin area
- Weakness or instability in the hip region
- Sciatica symptoms through back, hips and legs, like numbness, tingling, burning or pain
- Stiffness in the pelvic or hip region
These symptoms are often caused by inflammation to the joint from arthritis or other causes, like excess stress on the sacroiliac joint or hips.
Injection Treatments for Sacroiliac Joint Pain
One of the best treatments without invasive procedures is a sacroiliac joint injection. This procedure uses a fluoroscope and x-rays to find the joints and inject a pain reliever like lidocaine to the area, often accompanied by a corticosteroid. This can offer relief and help mitigate pain while the patient uses other options like physical therapy to strengthen and improve function.
Posted on behalf of:
Ortho Sport and Spine Physicians
5730 Glenridge Drive Northeast #230
Atlanta, GA 30328
(678) 752-7246
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
)